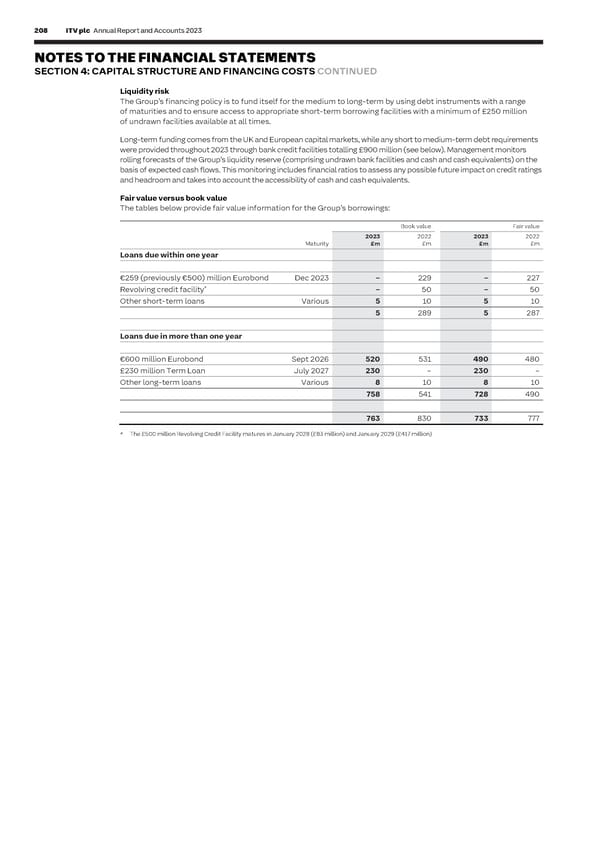
208 ITV plc Annual Report and Accounts 2023 ITV plc Annual Report and Accounts 2023 209 F I NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS NAN SECTION 4: CAPITAL STRUCTURE AND FINANCING COSTS CONTINUED C I AL Liquidity risk 4.3 Keeping What is a derivative? S T The Group’s financing policy is to fund itself for the medium to long-term by using debt instruments with a range it simple A derivative is a type of financial instrument typically used to manage risk. A A Managing T of maturities and to ensure access to appropriate short-term borrowing facilities with a minimum of £250 million derivative’s value changes over time in response to underlying variables, such as E market risks: M of undrawn facilities available at all times. exchange rates or interest rates and is entered into for a fixed period. A hedge is E derivative N where a derivative is used to manage exposure in an underlying variable. T Long-term funding comes from the UK and European capital markets, while any short to medium-term debt requirements financial S were provided throughout 2023 through bank credit facilities totalling £900 million (see below). Management monitors instruments The Group is exposed to certain market risks. In accordance with Board-approved rolling forecasts of the Group’s liquidity reserve (comprising undrawn bank facilities and cash and cash equivalents) on the policies, which are set out in this note, the Group manages these risks by using basis of expected cash flows. This monitoring includes financial ratios to assess any possible future impact on credit ratings derivative financial instruments to hedge the underlying exposures. and headroom and takes into account the accessibility of cash and cash equivalents. Why do we need them? Fair value versus book value The key market risks facing the Group are: The tables below provide fair value information for the Group’s borrowings: • Currency risk arising from: Book value Fair value i. Translation risk, that is the risk in the period of adverse currency fluctuations in the 2023 2022 2023 2022 translation of foreign currency profits, assets and liabilities (‘balance sheet risk’) Maturity £m £m £m £m and non-functional currency monetary assets and liabilities (‘income statement Loans due within one year risk’) and ii. Transaction risk, that is the risk that currency fluctuations will have a negative effect €259 (previously €500) million Eurobond Dec 2023 – 229 – 227 on the value of the Group’s non-functional currency trading cash flows. A non- * Revolving credit facility – 50 – 50 functional currency transaction is a transaction in any currency other than the Other short-term loans Various 5 10 5 10 reporting currency of the subsidiary 5 289 5 287 • Interest rate risk to the Group arises from significant changes in interest rates on borrowings issued at or swapped to floating rates Loans due in more than one year How do we use them? The Group mainly employs three types of derivative financial instruments when €600 million Eurobond Sept 2026 520 531 490 480 managing its currency and interest rate risk: £230 million Term Loan July 2027 230 – 230 – • Foreign exchange swap contracts are derivative instruments used to hedge Other long-term loans Various 8 10 8 10 income statement translation risk arising from short-term intercompany loans 758 541 728 490 denominated in a foreign currency • Forward foreign exchange contracts are derivative instruments used to hedge 763 830 733 777 transaction risk so they enable the sale or purchase of foreign currency at a known fixed rate on an agreed future date and * The £500 million Revolving Credit Facility matures in January 2028 (£83 million) and January 2029 (£417 million) • Cross-currency interest rate swaps are derivative instruments used to exchange the principal and interest coupons in a debt instrument from one currency to another Analysis of the derivatives used by the Group to hedge its exposure and the various methods used to calculate their respective fair values are detailed in this section. Accounting policies Derivative financial instruments are initially recognised at fair value and are subsequently remeasured at fair value with the movement recorded in the Consolidated Income Statement, except where derivatives qualify for cash flow hedge accounting. In this case, the effective portion of a cash flow hedge is recognised in other comprehensive income and presented in the hedging reserve within equity. The cumulative gain or loss is later reclassified to the Consolidated Income Statement in the same period as the relevant hedged transaction is realised. Derivatives with positive fair values are recorded as assets and negative fair values as liabilities.
 ITV Annual Report & Accounts Page 209 Page 211
ITV Annual Report & Accounts Page 209 Page 211